BIOS (Basic Input Output System)
- BIOS is the program a computer’s microprocessor uses to get the computer system started after you turn it on.
- It also manages data flow between the computer’s operating system and attached devices such as the hard disk, graphic card, keyboard, mouse and printer.
- BIOS is a chip located on all motherboard that contain instruction of how your system should boot and how it operate.
- The BIOS include instruction on how to load basic computer hardware & include a test referred as a POST that verifies the computer needs requirement to boot up properly.
- If the computer does not pass the POST, you will receive a combination of beep indication that indicates malfunctioning within the computer.
POST:
- POST is a test the computer must complete to verify all hardware is working properly before starting the remainder of the boot process.
- If the computer passes the POST the computer will often return a single beep and if unsuccessful will create a beep code that indicates the error.
What do you meant by the term ROM BIOS (Read Only Memory BIOS)?
- Read only means that the Program and data can only be read from it. Therefore Program and data cannot be written to it.
- Most Computer contain small amount of ROM to stores programs that enable the computer to boots.
- It is a non- volatile memory and hence it is referred as a permanent data storage area.
- The BIOS in a PC is stored on a ROM chip located on the motherboard.
- Early PCs used a ROM BIOS, but PCs today use a flash memory BIOS because it can be updated in place.
- In order to update a ROM BIOS, the computer case had to be opened, and the ROM chip had to be located and replaced.
How do I get to BIOS in Windows 7?
- Turn off the computer and wait five seconds.
- Now turn on the computer and immediately press the F10 key or F1 key three to four times after you see company logo on display until a BIOS Setup screen opens.
- In the BIOS Setup utility, do one of the following: On the Main tab, find the BIOS version.
Note: – Different Company models Had Different Keys to go in Bios Screen Option.
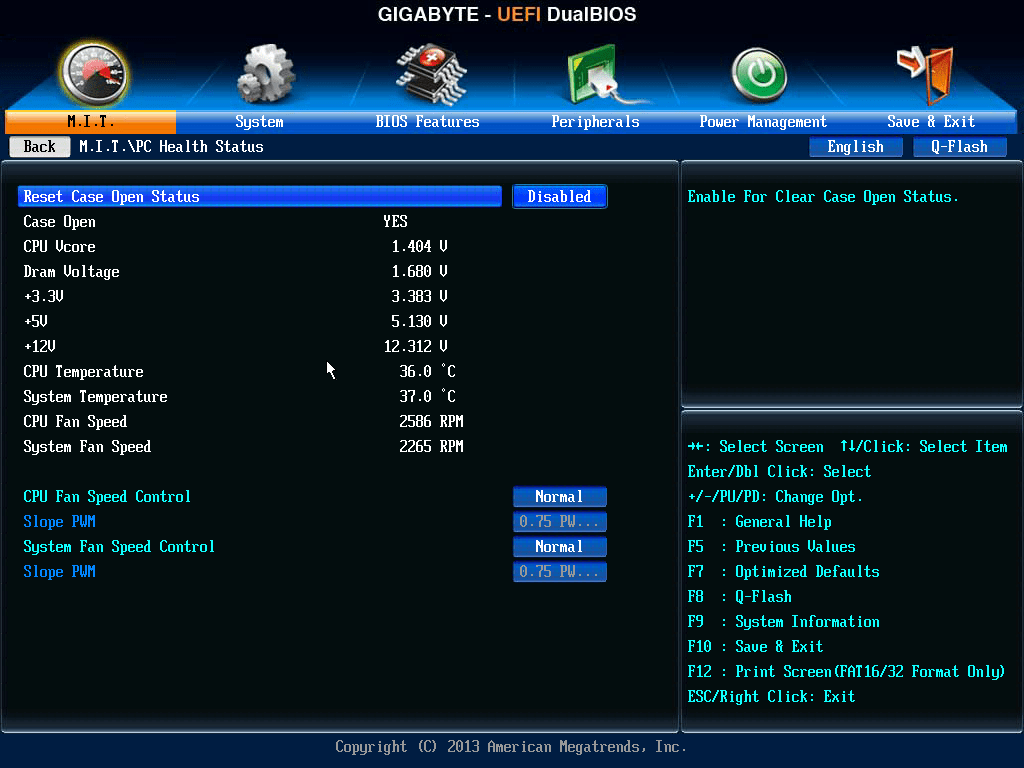
What do mean by Dual BIOS?
- Dual BIOS mean there are two ROM Bios IC Chip present on the Motherboard.
- A dual BIOS is a computer motherboard that contains a main BIOS and a backup BIOS.
- This type of setup can help a motherboard recover from any problems encountered during a BIOS update.
- It also helps protect the BIOS from any potential virus, or any other data corruption that might occur.
View BIOS information at POST
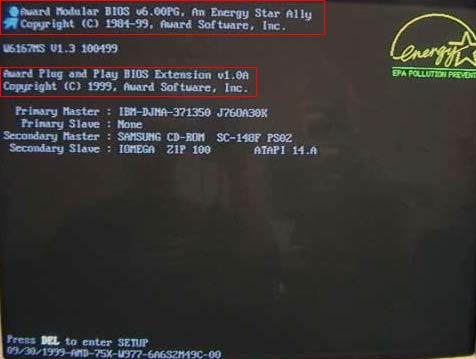
- The first way is by restarting your computer.
- When the initial load (also called POST) screen is displayed, the BIOS Type and version is also displayed.
Tip: If the load screen is displayed for only a few seconds, you can try pressing the Pause/Break key on your keyboard to pause the loading process.
- The BIOS information is typically found at or near the top of the POST screen.
- Also, you will see information on what hard drive(s) and CD/DVD drives are installed in your computer.
Through Windows System Information
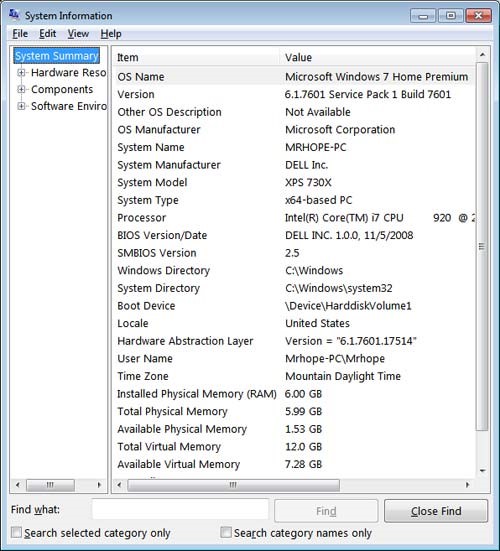
- The BIOS information is also shown through the Windows System Information.
- To open this tool click start, Programs, Accessories, System Tools, and then System Information.
- If you’re running Windows Vista or Windows 7, type System Information in the Start search box.
- In the System Information window, displaying information about your computer, including the type of BIOS you have and the version, under the System Summary section.
- As can be seen in the picture below, this computer has a DELL BIOS version 1.0.0 with a Date of 11/5/2008.
Windows Registry
- You can also find BIOS information in the Windows System Registry.
- While in the registry realize that improperly changing a setting can affect how Windows operates.
- To access the System Registry, click start and in the Run or Search box type reg edit in the text field and press enter. In the Windows Registry navigate to the below Registry directory.
Hkey_local_machine\hardware\description\system - Find the sub keys System Bios Date and System Bios Version to see the BIOS and version for your motherboard. As can be seen in the picture below, the BIOS date and version are shown in these two keys.
Types of BIOS: –
- Single Page BIOS.
- Multi Page BIOS/ Five Page BIOS.
- Explorer BIOS.
- Phoenix BIOS.
- UEFI BIOS (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface).
-
Single Page BIOS: –
- In Single Page Mode BIOS all the Option are in one single Page.
- It can be seen in early 90’s computer.
-
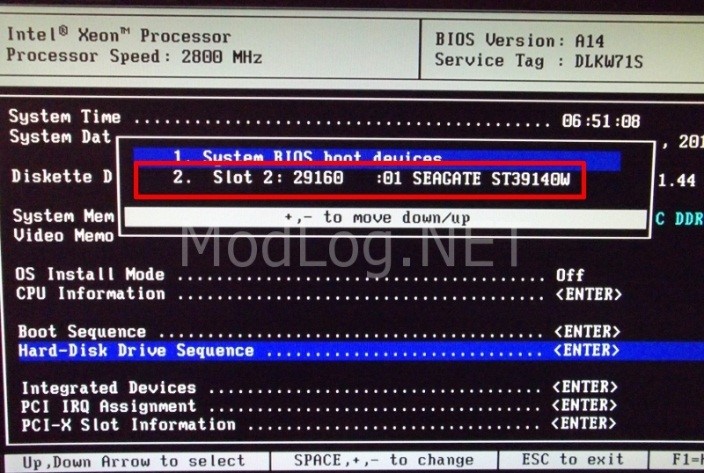
Multi / Five Page BIOS: –
- Multi page or Five page Mode BIOS has 5 different option namely Main, Advanced, Security, Boot, Exit.

-
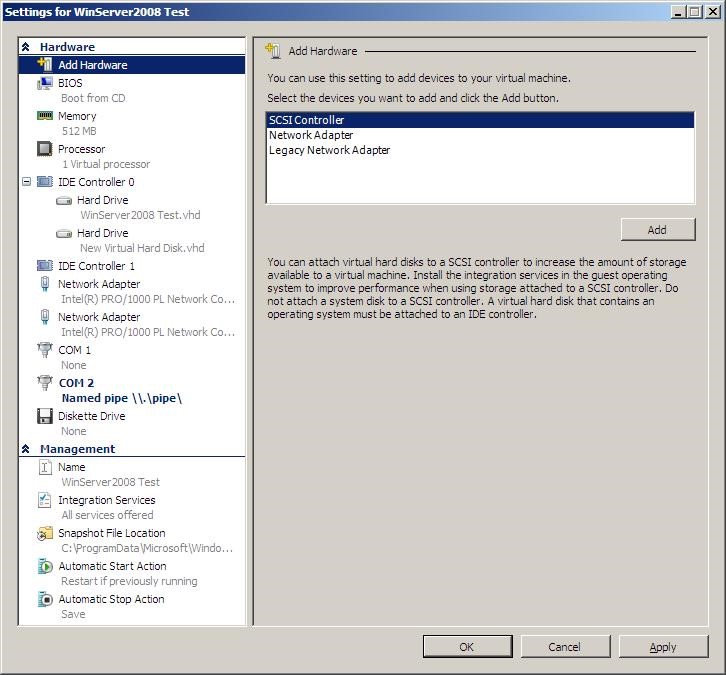
Explorer BIOS:-
- This BIOS is Windows Explorer Lookalike.
- It is the only BIOS where we can use Mouse.
-
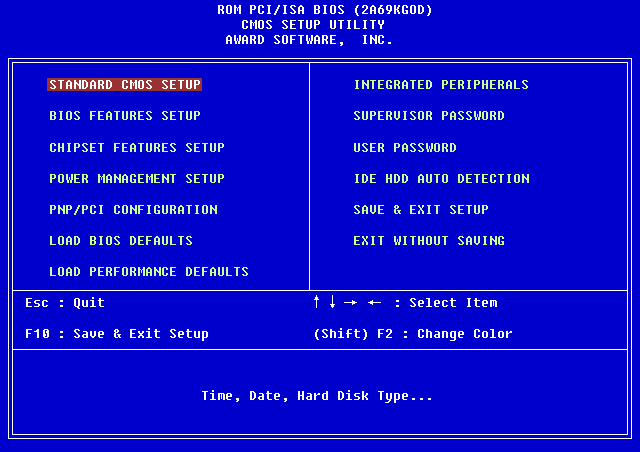
Phoenix BIOS : –
- Phoenix BIOS is the commonly see BIOS in nowadays new and old Computer.
-
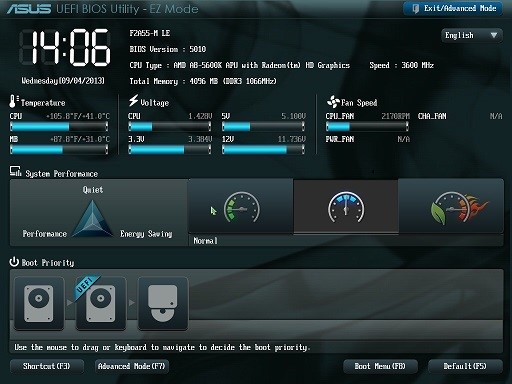
UEFI BIOS (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface): –
- UEFI Bios is the latest Bios used in new computer.
- UEFI Bios is mostly used in Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10.
- This bios help the computer to boot up faster than any other bios.